Burkina FasoDownload light PDF version
Overview
With its six bordering countries (Benin, Côte d'Ivoire, Ghana, Mali, Niger and Togo) all being members of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), Burkina Faso is at the geographic centre of the continental ECOWAS area. This may in part explain why such a large number of regional and international organisations and NGOs are located in the “country of honest men” (literal translation from Mooré of Burkina Faso). Burkina Faso hosts, for example, the headquarters of the West African Economic and Monetary Union (UEMOA), the Executive Secretariat of the Permanent Inter-State Committee for Drought Control in the Sahel (CILSS) and the Executive Secretary of the Volta Basin Authority (ABV). The Burkinabè government is also very involved in sub-regional diplomacy and has played a key role as mediator for neighbouring countries affected by political crises (namely, Côte d’Ivoire, Guinea and Togo).
Together, Burkina Faso, Côte d’Ivoire and Mali form the largest cotton basin in Africa. As a landlocked country, Burkina Faso is particularly dependant on regional transport corridors which link to ports in Abidjan, Cotonou, Dakar, Lomé and Tema. Intra-regional trade is an important driver of growth in Burkina Faso. A third of Burkina Faso’s recorded exports in 2008 were sent to UEMOA and ECOWAS member countries. With most agro-food business not recorded in official statistics, the numbers are certainly in reality much higher. In terms of energy policy, Burkina Faso also counts on regional co-operation to meet its energy needs. A high tension line between Bolgatanga, Ghana and Burkina Faso’s capital Ouagadougou is set to be launched in 2012 as part of the ECOWAS Power Pool Expansion Investment Plan.
Traditionally, Burkina Faso has a long history of migration with Côte d’Ivoire, particularly due to labour-intensive work in Côte d’Ivoire’s agricultural sector (on cocoa farms notably). It is estimated that about 2.5 million Burkinabè are residents in Côte d’Ivoire, including a large share of second and third generation immigrants who have often never been to their country of origin.
Institutional Framework
| Government type: | Parliamentary Republic |
| Constitution: | approved by referendum on 2 June 1991; formally adopted on 11 June 1991; last amended in January 2002. |
| Legal System: | civil law based on the French model and customary law |
| Administrative Division | 45 provinces; Bale, Bam, Banwa, Bazega, Bougouriba, Boulgou, Boulkiemde, Comoe, Ganzourgou, Gnagna, Gourma, Houet, Ioba, Kadiogo, Kenedougou, Komondjari, Kompienga, Kossi, Koulpelogo, Kouritenga, Kourweogo, Leraba, Loroum, Mouhoun, Nahouri, Namentenga, Nayala, Noumbiel, Oubritenga, Oudalan, Passore, Poni, Sanguie, Sanmatenga, Seno, Sissili, Soum, Sourou, Tapoa, Tuy, Yagha, Yatenga, Ziro, Zondoma, Zoundweogo |
| Executive Branch: |
|
| Legislative Branch: | unicameral National Assembly or Assemblee Nationale (111 seats; members are elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms) |
| Judical Branch: | Supreme Court of Appeals or Cour de Cassation; Council of State or Conseil d'Etat; Court of Accounts or la Cour des Comptes; Constitutional Council or Conseil Constitutionnel |
| Main Political Parties: |
|
| Suffrage: | 18 years of age; universal |
| Elections: | president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 21 November 2010 (next to be held in 2015); prime minister appointed by the president with the consent of the legislature |
| Election Results: | Blaise COMPAORE reelected president; percent of popular vote - Blaise COMPAORE 80.2%, Hama Arba DIALLO 8.2%, Benewende Stanislas SANKARA 6.3%, other 5.3% |
| Central Bank: | Central Bank of West African States (BCEAO) |
| Military Branches |
|
| Military Age and Obligations: | 18 years of age for voluntary military service; women may serve in supporting roles (2011) |
| Membership in Regional Organisations | ECOWAS, UEMOA, CILSS, ABN, ABV, Ced-sad |
Source: CIA Factbook
Regional Indicators
| Land boundaries: | 3 192 km |
| Border countries: | Benin (306 km), Côte d'Ivoire (584 km), Ghana (549 km), Mali (1 000 km), Niger (628 km), Togo (126 km) |
| Coastline: | 0 (landlocked) |
| Airports: | 24 (2010) including 2 with paved runways |
| Railways: | 622 km |
| Roadways: | 92 495 km paved: 3 857 km unpaved: 88 638 km (2004) |
| Waterways: | - |
| Ports and terminals: | - |
Source: CIA Factbook and others
Demographic Trends
| Population 2010: | 16.3 million |
| Projection 2050: | 46.7 million |
| Population < 15 years (2010): | 7.1 million (= 45.3% of total population) |
| Population density: | 60/km2 |
| Urban agglomeration: | Ouagadougou (1.4 million, Africapolis) |
| Annual growth: | 2.97 % (2005-2010) |
| Total fertility rate (births per woman): | 6.46 (2005-2010) |
| Median age: | 16.3 years |
| Dependency ratio: | 97 |
2010 | 2020 | 2030 | |
| <15 years (%) | 47.1 | 45.6 | 42.5 |
| 15-64 years | 50.7 | 52.3 | 55.3 |
| > 65 years | 2.2 | 2.1 | 2.2 |
| Rural population | 64.1 | 56.3 | 48.7 |
| Urban population | 35.9 | 43.7 | 51.3 |
Source: World Populations Prospects, 2008 Revision
Migration and Mobility
| Number of emigrants (2010): | 1 576 400 = 9.7% of total population |
| Number of immigrants (2010): | 104 300 = 6.4% of total population |
| Top destination countries: | Côte d’Ivoire, Niger, Mali, Italy, Benin, Nigeria, France, Gabon, Germany, the United States |
| Top source countries: | Côte d’Ivoire, Mali, Ghana, Togo, Niger, Benin |
| Refugees within country: | 600 (2009) |
Economic Indicators
| GDP PPP (2010): | USD 20 986 million |
| % of West Africa | 3.5% |
| GDP per capita: | USD 1 289 |
| Annual growth (2010): | 5.7% |
| Average growth (2002-2012): | 5.5% |
| Currency | F CFA |
| WB Income group: | Low income |
| Inflation rate: | 0.9% |
| Trade balance | USD -483 million |
| FDI inflows (2009): | USD 171 million |
| External debt (2009): | USD 1931 million = 4.6% of GDP |
| Debt service (as % of exports 2010e): | 4.9% |
Public finance (% of GDP 2009): |
|
| Main exports: | Cotton, livestock, gold |
| Main imports: | Capital goods, foodstuffs, petroleum |
| Main export partners: | China 21.2%, Singapore 15%, Belgium 11.4%, Ghana 6.1%, Denmark 5.1%, Niger 4.6%, Thailand 4% (2009) |
| Main import partners: | Côte d’Ivoire 24.7%, France 19.8%, Togo 5% (2009) |
| Labour force participation (2008): | 79.7% Female; |
| Child labour (% of children ages 5–14) 1999–2007: | 47 |
| Diaspora Remittances 2009e: |
|
ODA received: |
|
Military Expenditures: |
|
| IMF Adjustment Programme | yes |
| Corruption Perception Index (2010): | 3.1 (rank 98 out of 178 countries) |
| Index of Economic Freedom 2011: | 60.6 (rank 85 out of 179 countries) |
| WB Doing Business Index (2011): | Rank 150 out of 183 countries |
| Ibrahim African Governance Index (2011): | Rank 19 out of 53 countries |
Sources: African Economic Outlook - CIA Factbook - Various Indexes
Food Security
| Global Hunger Index (IFPRI, 2011): | 17.2 |
| Food supply (kcal per capita/day) | 2 669 |
| Number of people undernourished: | 1.2 million |
:Percentage of people undernourished: | 9% |
| Child malnutrition, underweight: | 37% |
| Child malnutrition, stunting: | 35% |
Land use
| Land area (1000 ha): | 27 360 |
| Agricultural land area (1 000 ha):: | 11 965 |
Arable land (1 000 ha): | 6 300 |
| Permanent crops (1 000 ha): | 60 |
| Pastures (1 000 ha): | 6 000 |
| Irrigated land (1 000 ha): | 30 |
| Share in total water use by |
|
| Forest area (1000 ha): | 5 649 |
Source: FAOStat (2009) and FAO Country Profile
Social Indicators
| Ethnic groups | Mossi over 40%, other approximately 60% (includes Gurunsi, Senufo, Lobi, Bobo, Mande, and Fulani) |
| Major religions | Muslim 60.5%, Catholic 19%, animist 15.3%, Protestant 4.2%, other 0.6%, none 0.4% |
Health
| Public expenditure on health (% of GDP) | 3.4% |
| Infant mortality rate (per 1 000 live births) | 92 |
| Under-five mortality rate (per 1 000 live births) | 166 |
| Number of physicians (for 100 000 people) (2004) | 2.1 |
| Hospital beds (for 10 000 people) | 9 (2006) |
| Estimated HIV prevalence (2007) | 1.6% |
| Death rates associated with Malaria: |
|
Education
| Public expenditure on education (% of GDP): | 4.6% |
| Expected years of schooling (of children under 7) | 6.3 years |
| Mean years of schooling (of adults over 25) | 1.3 years |
| Adult literacy rate (% aged 15 and above) | 28.7% (2007) |
| Youth literacy rate | 39.3% (2008) |
| Primary enrolment (% both sexes) | 64.4% |
| Net secondary Enrolment: | 467 658 students (2009) |
| University attendance ratio: | 3.4% (2009) |
| Universities: | 5 public and 2 private universities |
ICT
| Internet access (per 100 inhabitants) 2009: | 1.13 |
| Internet domain: | bf |
| International dialing code: | 226 |
| Mobile line (per 100 inhabitants) 2009: | 24.27 |
| Main telephone line (per 100 inhabitants) 2009: | 0.97 |
Access to Basic Services
| Access to Electricity 2007: | kWh 727 millions |
| Water Supply Coverage (2008): | 76% (urban 95%, rural 72%) |
| Sanitation Coverage (2008): | 11% (urban 33%, rural 6%) |
Sources : UNDP Human Development Report 2011, CIA Factbook, others
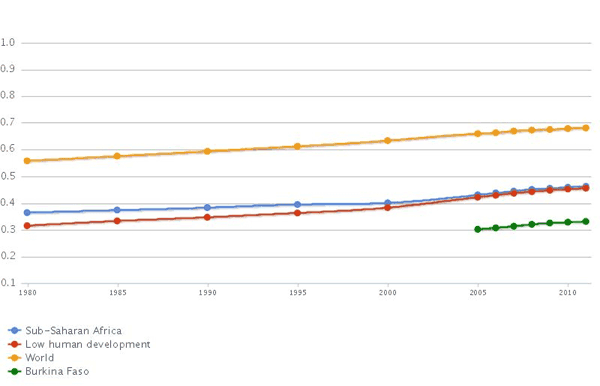
MDG Tracking