BeninDownload light PDF version
Overview
With a 2 000 km border and almost all of its population living a maximum of 100 km away from the border, this small coastal country is highly dependent upon the regional market, in particular on trade with Nigeria. According to 2010 estimates, between 6.5 and 7.5% of Benin’s GDP is derived from its trade with Nigeria, and informal sector trade largely exceeds these official figures. In addition, the crisis in Côte d’Ivoire has provided incentive for developing alternative links between landlocked West African countries and the coast, increasing the importance of the Cotonou as a regional port deserving Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger.
Benin is also largely dependent on neighbouring countries for electricity imports. Major power shortages in the country are frequent as the national power demand largely exceeds the generation capacity of the government-controlled electric company “Société béninoise d’électricité et d’eau” (SBEE). The headquarters of the ECOWAS West African Power Pool (WAPP) has been based in Cotonou since 1999.
Other transnational issues that require regional co-operation include: joint management of the “W” Transborder Park with Burkina Faso and Niger; joint management of the Niger River basin with Burkina Faso, Chad, Côte d’Ivoire, Guinea, Mali, Niger and Nigeria; and the improvement of transport corridors, notably the Abidjan-Accra-Lomé-Cotonou-Lagos corridor linking Benin to Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana, Nigeria and Togo.
Benin was hit by the worst flooding in 50 years in September and October 2010 causing considerable damages. The flooding affected about two-thirds of the country and generated a wave of solidarity across West Africa.
Institutional Framework
| Government type: | Republic |
| Constitution: | adopted by referendum 2 December 1990 |
| Legal System: | civil law system modeled largely on the French system and some customary law |
| Administrative Division | 12 departments: Alibori, Atakora, Atlantique, Borgou, Collines, Kouffo, Donga, Littoral, Mono, Oueme, Plateau and Zou |
| Executive Branch: |
|
| Legislative Branch: | unicameral National Assembly (83 seats; members are elected by direct popular vote to serve four-year terms) |
| Judical Branch: | Constitutional Court; Supreme Court; High Court of Justice |
| Main Political Parties: |
|
| Suffrage: | 18 years of age; universal |
| Elections: | president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); last held on 13 March 2011 (next to be held in March 2016) |
| Election Results: | Thomas YAYI Boni re-elected president; percent of vote - Thomas YAYI Boni 53.1%, Adrien HOUNGBEDJI 35.6%, Abdoulaye Bio TCHANE 6.1%, other 5.2% |
| Central Bank: | Central Bank of West African States (BCEAO) |
| Military Branches |
|
| Military Age and Obligations: | 21 years of age for compulsory and voluntary military service; in practice, volunteers may be taken at the age of 18; both sexes are eligible for military service; conscript tour of duty - 18 months (2006) |
| Membership in International Organisations | UEMOA, ECOWAS, ABN, ABV, WADB, AU, AfDB, Cen-Sad |
Regional Indicators
| Land Boundaries: | 1989 km |
| Border Countries: | Burkina Faso: 306 km; Niger: 266 km; Nigeria: 773 km; Togo: 644 km |
| Coastline: | 121 km |
| Airports: | 5 with paved runways: 1 |
| Railways: | 438 km |
| Roadways: | 16,000 km, paved: 1,400 km |
| Waterways: | 150 km (2010) |
| Ports and Terminals: | Cotonou |
Demographic Trends
| Population 2010: | 9.2 million, = 2.8% of West Africa's population |
| Projection 2050: | 21.7 million |
| Population < 15 years (2010): | 3.9 million, = 43.7% |
| Population density: | 79/ sq km |
| Urban agglomeration: | Cotonou, 1.3 million (Africapolis) |
| Annual Growth: | 2.96% (2005-2010) > 2.7% (2010-2015) |
| Total Fertility Rate (births per woman): | 5.48 (2005-2010) > 5.08 (2010-2015) |
| Median age: | 17.9 years |
| Dependency ratio: | 135 (2010) |
2010 | 2020 | 2030 | |
| <15 years (%) | 43.7 | 41.6 | 38.4 |
| 15-64 years | 53.3 | 55.3 | 58 |
| > 65 years | 3.0 | 3.1 | 3.6 |
| Rural Population | 58 | 52.8 | 46.3 |
| Urban Population | 42 | 47.2 | 53.7 |
Source: World Population Prospects, 2008 Revision,http:esa.un.org/unpp
Migration and Mobility
| Number of Emigrants (2010): | 531 600 people = 5.8% of total population |
| Number of Immigrants (2010): | 232 000 people = 2.5% of total population |
| Top Destination Countries: | Nigeria, Togo, Côte d’Ivoire, Gabon, Niger, France, Burkina Faso, Republic of Congo, Italy, Guinea |
| Top Source Countries: | Niger, Togo, Nigeria, Burkina Faso, France |
| Refugees within country: | 6 900 (2009) |
Source: The World Bank Remittances and Migration Fact Book 2011.
Economic Indicators
| GDP PPP (2010): | USD 13 833 million |
| % of West Africa | 2.3% |
| GDP per capita: | USD 1502 |
| Annual Growth (2009): | 2.7% |
| Average Growth (2002-2012): | 3.6% |
| Currency | F CFA |
| Income Group (WB): | low income |
| Inflation Rate: | 2.2 (2009) |
| Trade Balance | USD -797 million |
| FDI Inflows (2009): | USD 93 million |
| External Debt (2009): | USD 1 141 million = 4.5% of GDP |
| Debt Service (as % of exports 2010e): | 6.3% |
Public Finance (% of GDP 2009): |
|
| Main Exports: | cotton, cashews, shea butter, textiles, palm products, seafood |
| Main Imports: | foodstuffs, capital goods, petroleum products |
| Main Export Partners: | India (26%), China (20.7%), Niger (6.7%), Nigeria (6.3%), Namibia (4%) (2009) |
| Main Import Partners: | China (35.8%), USA (7.3%), France (7.2%), Thailand (6.5%), Malaysia (5.5%), The Netherlands (4.7%) (2009) |
| Labour force participation (2008): | 68.1% Female; 79% Male |
| Child labour (% of children ages 5–14) 1999–2007: | 46% |
| Diaspora Remittances 2009e: |
|
ODA received: |
|
Public Spending on Education, % of total (2000-2007): |
|
| Public Sepnding on Health, % of total (WHO, 2009): |
|
Military Expenditures: |
|
| IMF Adjustment Programme | yes |
| Corruption Perception Index: | 2.8 (110/178) |
| Index of Economic Freedom 2011: | 56 (117/179) |
| WB Doing Business Index (2011): | 173 out of 183 countries |
| Ibrahim African Governance Index: | 62.5 |
Food Security
| Global Hunger Index (IFPRI, 2011): | 14.7 |
| Food supply (kcal per capita/day) | 2 512 |
| Number of people undernourished: | 1 million |
:Percentage of people undernourished: | 12% |
| Child malnutrition, underweight: | 23% |
| Percentage of infants with slowed growth rate: | 38% |
Land use
| Land area (1 000 ha): | 11 006 |
| Agricultural land area (1 000 ha): | 3 300 |
Arable land (1 000 ha): | 2 550 |
| Permanent crops (1 000 ha): | 295 |
| Pastures (1 000 ha): | 550 |
| Irrigated land (1 000 ha): | 12 |
| Share in total water use by |
|
| Forest area (1000 ha): | 4 561 |
Source: FAOStat and FAO Country Profile
Social Indicators
| Ethnic Groups |
|
| Major Religions |
|
Health
| Public Expenditure on Health (% of GDP) | 2.5% |
| Infant Mortality Rate (per 1 000 live births) | 76 |
| Under-five Mortality Rate (per 1 000 live births) | 118 |
| Number of Physicians (for 100 000 people) (2004) | 11.4 |
| Hospital Beds (for 10 000 people) | 5 (2005) |
| 60 000 people [52 000 - 69 000] |
| Adults aged 15 to 49 prevalence rate | 1.2% [1% - 1.3%] |
Orphans due to AIDS aged 0 to 17 | 30 000 orphans [18 000 - 53 000] |
| Malaria Death Rates (2009) | 1 375 people, including 1 157 < 5 years |
Education
| Public Expenditure on Education (% of GDP): | 3.5% |
| Expected years of schooling (of children under 7) | 9.2 |
| Mean years of schooling (of adults over 25) | 3.3 |
| Adult Literacy Rate (% aged 15 and above) | 41.7 |
| Youth Literacy Rate | 53.3 |
| Primary Enrolment (% both sexes) | 92.8% |
| Net Secondary Enrolment: | |
| University attendance Ratio: | 6,1% (2004) |
| Universities: | 17 universities (2 public; 15 private) |
ICT
| Internet Access (per 100 inhabitants) 2009: | 2.24 |
| Internet Domain: | bj |
| International Dialing Code: | 229 |
| Mobile Line (per 100 inhabitants) 2009: | 56.33 |
| Main Telephone Line (per 100 inhabitants) 2009: | 1.42 |
Access to Basic Services
| Access to Electricity 2007: | |
| Water Supply Coverage (2008): | 75% (urban 84%, rural 69%) |
| Sanitation Coverage (2008): | 12% (24% urban, 4% rural) |
MDG Tracking
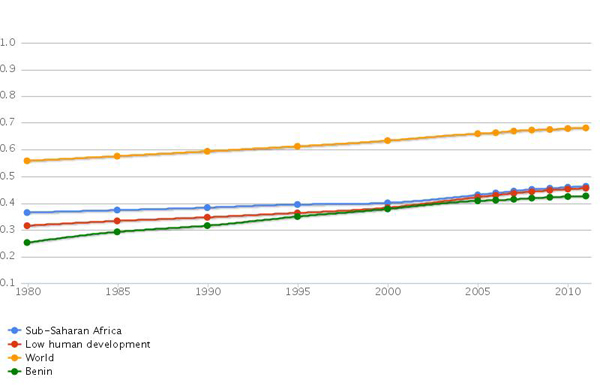
Human Development Index: Trends 1980 - present